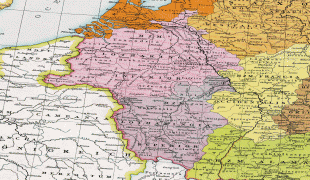
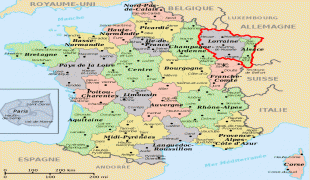
Lorraine (Lorraine)
 |
 |
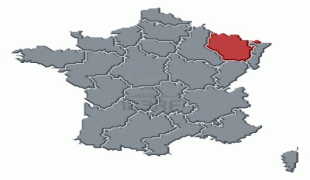
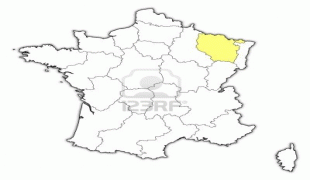
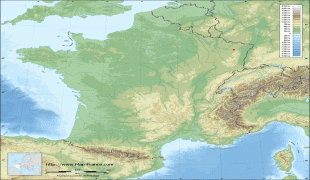
From 1982 until January 2016, Lorraine was an administrative region of France. In 2016, under a reorganisation, it became part of the new region Grand Est. As a region in modern France, Lorraine consisted of the four departments Meurthe-et-Moselle, Meuse, Moselle and Vosges (from a historical point of view the Haute-Marne department is located in the region), containing 2,337 communes. Metz is the regional prefecture. The largest metropolitan area of Lorraine is Nancy, which had developed for centuries as the seat of the duchy.
Lorraine borders Germany, Belgium, and Luxembourg. Its inhabitants are called Lorrains and Lorraines in French and number about 2,356,000.
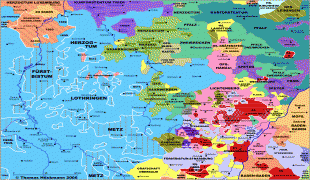
Lorraine's borders have changed often in its long history. The location of Lorraine led to it being a paramount strategic asset as the crossroads of four nations. This, along with its political alliances, marriage alliances, and the ability of rulers over the centuries to choose sides between East and West, gave it a tremendously powerful and important role in transforming all of European history. Its rulers intermarried with royal families over all of Europe, played kingmaker, and seated rulers on the thrones of the Holy Roman Empire and the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and others.
In 840, Charlemagne's son Louis the Pious died. The Carolingian Empire was divided among Louis' three sons by the Treaty of Verdun of 843. The middle realm, known as Middle Francia, went to Lothair I, reaching from Frisia in Northern Germany through the Low Countries, Eastern France, Burgundy, Provence, Northern Italy, and down to Rome. On the death of Lothair I, Middle Francia was divided in three by the Treaty of Prüm in 855, with the northern third called Lotharingia and going to Lothair II. Due to Lotharingia being sandwiched between East and West Francia, the rulers identified as a duchy from 870 onward, enabling the duchy to ally and align itself nominally with either eastern or western Carolingian kingdoms in order to survive and maintain its independence. Thus, it was a duchy in name but operated as an independent kingdom.
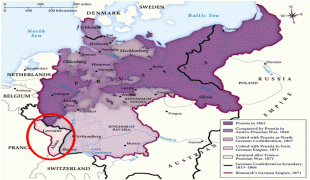
In 870, Lorraine allied with East Francia while remaining an autonomous duchy. In 962, when Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor, restored the Empire (restauratio imperii), Lorraine was designated as the autonomous Duchy of Lorraine within the Holy Roman Empire. It maintained this status until 1766, after which it was annexed under succession law by the Kingdom of France, via derivative aristocratic house alliances.
The succession within these houses, in tandem with other historical events, would have later restored Lorraine's status as its own duchy, but a vacuum in leadership occurred. Its duke Francois Stephen de Lorraine took the throne of the Holy Roman Empire as Francis I, and his brother Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine became governor of the Austrian Netherlands. For political reasons, he decided to hide those heirs who were not born by his first wife, Archduchess Maria Anna of Austria, who was deceased when he took office.
The vacuum in leadership, the French Revolution, and the political results and changes issuing from the many nationalistic wars that followed in the next 130 years, ultimately resulted in Lorraine becoming a permanent part of the modern Republic of France. Because of wars, it came under control of Germany several times as the border between the nations shifted. While Lorrainian separatists do exist in the 21st century, their political power and influence is negligible. Lorraine separatism today consists more of preserving its cultural identity rather than seeking genuine political independence.
With enlightened leadership and at a crossroads between French and German cultures, Lotharingia experienced tremendous economic, artistic, and cultural prosperity during the 12th and 13th centuries under the Hohenstaufen emperors. Along with the rest of Europe, this prosperity was terminated in Lorraine in the 14th century by a series of harsh winters, bad harvests, and the Black Death. During the Renaissance, a flourishing prosperity returned to Lotharingia until the Thirty Years' War.
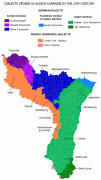
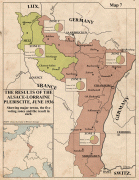
France inherited Lorraine in 1766. Due to the region's location, the population has been mixed. The north is largely German, speaking Lorraine Franconian and other German dialects. Strong centralized nationalism had only begun to replace the feudalist system which had formed the multilingual borders, and insurrection against the French occupation influenced much of the area's early identity. In 1871, the German Empire regained a part of Lorraine (Bezirk Lothringen, corresponding to the current department of Moselle). The department formed part of the new German Empire's Imperial Territory of Alsace–Lorraine. In the French Third Republic, the revanchist movement developed to recover this territory.
Map - Lorraine (Lorraine)
Map
Country - France
 |
 |
| Flag of France | |
Inhabited since the Palaeolithic era, the territory of Metropolitan France was settled by Celtic tribes known as Gauls during the Iron Age. Rome annexed the area in 51 BC, leading to a distinct Gallo-Roman culture that laid the foundation of the French language. The Germanic Franks formed the Kingdom of Francia, which became the heartland of the Carolingian Empire. The Treaty of Verdun of 843 partitioned the empire, with West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France in 987. In the High Middle Ages, France was a powerful but highly decentralised feudal kingdom. Philip II successfully strengthened royal power and defeated his rivals to double the size of the crown lands; by the end of his reign, France had emerged as the most powerful state in Europe. From the mid-14th to the mid-15th century, France was plunged into a series of dynastic conflicts involving England, collectively known as the Hundred Years' War, and a distinct French identity emerged as a result. The French Renaissance saw art and culture flourish, conflict with the House of Habsburg, and the establishment of a global colonial empire, which by the 20th century would become the second-largest in the world. The second half of the 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Huguenots that severely weakened the country. France again emerged as Europe's dominant power in the 17th century under Louis XIV following the Thirty Years' War. Inadequate economic policies, inequitable taxes and frequent wars (notably a defeat in the Seven Years' War and costly involvement in the American War of Independence) left the kingdom in a precarious economic situation by the end of the 18th century. This precipitated the French Revolution of 1789, which overthrew the Ancien Régime and produced the Declaration of the Rights of Man, which expresses the nation's ideals to this day.
Currency / Language
| ISO | Currency | Symbol | Significant figures |
|---|---|---|---|
| EUR | Euro | € | 2 |
| ISO | Language |
|---|---|
| EU | Basque language |
| BR | Breton language |
| CA | Catalan language |
| CO | Corsican language |
| FR | French language |
| OC | Occitan language |